Choisir le bon système de caméras de sécurité implique d'évaluer vos besoins, de choisir entre des modèles intérieurs et extérieurs, et de sélectionner des fonctionnalités clés comme la résolution vidéo (1080p, 2K ou 4K), l'alimentation (filaire ou sans fil) et le stockage (local ou cloud). Pensez aux fonctionnalités avancées d'intelligence artificielle pour des alertes plus pertinentes et déterminez si vous préférez une installation par vos soins ou par un professionnel. Le système idéal offre un équilibre entre performance, facilité d'utilisation et coût pour une surveillance efficace et une tranquillité d'esprit assurée pour votre propriété.

Table des matières
- Quels sont vos principaux objectifs en matière de sécurité ?
- Où allez-vous placer les caméras ?
- Comment les caméras seront-elles alimentées et connectées ?
- Quelles sont les qualités et fonctionnalités vidéo essentielles ?
- Comment vos enregistrements seront-ils stockés ?
- Quelles sont les fonctionnalités intelligentes qui comptent vraiment ?
- Qui installera le système ?
- Quels sont les coûts à long terme ?
Quels sont vos principaux objectifs en matière de sécurité ?
Avant d'aborder les spécifications techniques, la première étape consiste à définir vos objectifs pour votre système de caméras de sécurité . Vos motivations influenceront directement le type de système dont vous avez besoin. Cherchez-vous avant tout à dissuader les intrus potentiels ? Dans ce cas, des caméras extérieures bien visibles pourraient être votre priorité. Peut-être souhaitez-vous principalement surveiller l'intérieur de votre maison et veiller sur vos enfants, vos proches âgés ou vos animaux de compagnie. Dans ce cas, vous opterez pour des caméras intérieures avec audio bidirectionnel et fonction panoramique/inclinaison.

Vous pouvez aussi souhaiter recueillir des preuves de qualité en cas d'intrusion. Cela nécessite des caméras haute résolution, une excellente vision nocturne et un enregistrement fiable. Certains utilisateurs souhaitent simplement surveiller la réception de leurs colis pour prévenir les vols. Une sonnette vidéo ou une caméra dotée d'une fonction de détection de colis serait alors idéale. Définir clairement vos objectifs ( dissuasion, surveillance, collecte de preuves ou gestion de tâches spécifiques ) vous permettra de cibler vos options et d'investir dans un système adapté à vos besoins de sécurité.
Où allez-vous placer les caméras ?
L'environnement physique dans lequel vos caméras seront utilisées est un facteur déterminant. Les caméras sont conçues différemment pour une utilisation intérieure et extérieure, avec des caractéristiques spécifiques adaptées à leur environnement. Un mauvais choix peut endommager le matériel ou nuire à ses performances.
Choisir des caméras d'intérieur
Les caméras d'intérieur sont conçues pour un usage domestique. Plus petites et discrètes, elles sont principalement destinées à la surveillance des espaces de vie. La fonction panoramique et d'inclinaison est un critère essentiel : elle permet à une seule caméra de couvrir une large zone, comme un salon ou une cuisine ouverte, en pivotant horizontalement et verticalement. Cette solution est plus économique que l'installation de plusieurs caméras fixes.
L'audio bidirectionnel est une autre fonctionnalité essentielle pour les modèles d'intérieur, vous permettant de communiquer à distance avec vos proches ou vos animaux de compagnie. Le respect de la vie privée est également primordial pour les caméras d'intérieur. Privilégiez les modèles équipés d'un obturateur physique ou d'un « mode maison » qui désactive l'enregistrement lorsque vous êtes présent. Installez-les de préférence dans les zones de passage comme les entrées, les couloirs et les pièces à vivre principales, en évitant les espaces privés tels que les chambres et les salles de bain.
Choisir des caméras extérieures
Les caméras extérieures constituent votre première ligne de défense et doivent être conçues pour résister aux intempéries. La spécification la plus importante à vérifier est l' indice de protection (IP) . Cet indice se compose de deux chiffres : le premier indique la protection contre les corps solides (comme la poussière), et le second, la protection contre les liquides (comme la pluie). Un indice IP65 ou supérieur est recommandé pour les caméras extérieures, garantissant leur étanchéité à la poussière et leur résistance aux jets d'eau de toutes directions.
L'éclairage extérieur est également plus variable. C'est pourquoi les caméras extérieures doivent être dotées d'une vision nocturne performante et d'une fonction WDR (Wide Dynamic Range), qui permet d'équilibrer les scènes présentant une forte luminosité et des zones d'ombre importantes. Leur emplacement doit couvrir tous les principaux points d'accès à votre maison, notamment la porte d'entrée, la porte arrière et les fenêtres du rez-de-chaussée, ainsi que les garages ou abris de jardin.
Comment les caméras seront-elles alimentées et connectées ?
Choisir entre un système filaire et un système sans fil est une décision cruciale. Ce choix influence la complexité de l'installation, la fiabilité et la flexibilité d'emplacement.
Plaidoyer pour les systèmes sans fil et sans fil
Les caméras sans fil transmettent leur signal vidéo via votre réseau Wi-Fi. Cela simplifie l'installation, car vous n'avez pas besoin de faire passer de câbles réseau dans vos murs. Cependant, elles nécessitent toujours une source d'alimentation. C'est là qu'intervient le terme « sans fil ». Les caméras sans fil sont une catégorie particulière de caméras sans fil alimentées par des batteries rechargeables, ce qui les rend très faciles à installer. Vous pouvez les placer pratiquement n'importe où dans la zone de couverture Wi-Fi, sans vous soucier de la proximité d'une prise électrique.
En contrepartie de cette commodité, il est nécessaire de recharger les batteries régulièrement. Leur autonomie peut varier de quelques semaines à plusieurs mois, selon l'utilisation et les réglages. Certains modèles sans fil proposent des panneaux solaires en option pour une alimentation continue, une solution idéale pour les endroits extérieurs difficiles d'accès.
La fiabilité des systèmes câblés
Les caméras de sécurité filaires sont connectées par des câbles physiques pour l'alimentation et la transmission des données. L'alimentation par Ethernet (PoE) est une solution filaire répandue : un seul câble Ethernet fournit à la fois une connexion Internet stable et l'alimentation électrique de la caméra. Cette configuration est particulièrement fiable, car elle n'est pas affectée par les coupures ou les interférences du signal Wi-Fi.
Le principal inconvénient des systèmes câblés réside dans leur installation. Le passage des câbles à travers les murs et les plafonds peut s'avérer complexe et fastidieux, nécessitant souvent l'intervention d'un professionnel. Toutefois, pour une installation permanente et de grande envergure où une fiabilité maximale est primordiale, un système câblé reste souvent la meilleure solution.
| Type d'appareil photo | Avantages | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Câblé (PoE) | Connexion extrêmement fiable ; aucune inquiétude concernant la batterie ; bande passante plus élevée pour la vidéo 4K | Installation complexe ; options d’emplacement limitées ; coût initial d’installation plus élevé |
| Sans fil | Installation plus facile qu'avec un câblage ; placement flexible à proximité des prises de courant | Nécessite une prise de courant ; sensible aux interférences Wi-Fi ; peut saturer le réseau Wi-Fi |
| Sans fil (batterie) | Installation ultra-simple ; peut être placé n’importe où ; grande flexibilité | Les batteries nécessitent d'être rechargées ; durée d'enregistrement réduite pour économiser l'énergie ; les performances dépendent du Wi-Fi. |
Quelles sont les qualités et fonctionnalités vidéo essentielles ?
La fonction principale d'une caméra de sécurité est de capturer des vidéos nettes et exploitables. Plusieurs spécifications techniques déterminent la qualité de l'image affichée.
Décryptage de la résolution vidéo : la 4K est-elle nécessaire ?
La résolution vidéo détermine le niveau de détail de votre séquence. Elle est mesurée en pixels, et les options les plus courantes sont :
- 1080p (Full HD) : Longtemps, ce format a constitué la norme. Il offre une qualité vidéo suffisamment nette pour la surveillance courante.
- 2K (QHD) : Cette résolution offre une nette amélioration par rapport à la 1080p, vous permettant de voir plus de détails, tels que les visages ou les plaques d'immatriculation, à une plus grande distance.
- 4K (UHD) : Il s’agit de la plus haute résolution généralement disponible sur les appareils photo grand public. L’incroyable niveau de détail permet un zoom numérique important sans pixellisation de l’image. C’est particulièrement utile pour couvrir de grandes surfaces comme une allée ou un jardin.
Si la résolution 1080p peut suffire pour les petits espaces intérieurs, une résolution 2K ou 4K est fortement recommandée pour une utilisation en extérieur ou pour couvrir de grandes surfaces intérieures où il est important d'identifier les détails à distance.
Comprendre le champ de vision et le type d'objectif
Le champ de vision (FoV) , mesuré en degrés, détermine la zone couverte par la caméra. Un FoV plus large (par exemple, de 130° à 160°) permet à une seule caméra de couvrir une plus grande surface, réduisant ainsi potentiellement le nombre total de caméras nécessaires. Cependant, les angles très larges peuvent provoquer un effet « œil-de-poisson », déformant l'image sur les bords. Un FoV standard se situe généralement entre 110° et 130°. Pour la surveillance d'une zone spécifique et étroite, comme un couloir, un FoV plus étroit est parfaitement acceptable.
Voir dans le noir : qu'est-ce qu'une bonne caméra de vision nocturne ?
Les menaces à la sécurité ne cessent pas avec le coucher du soleil ; une vision nocturne efficace est donc indispensable. Il en existe deux principaux types :
- Vision nocturne infrarouge (IR) : C’est le type le plus courant. La caméra utilise des LED infrarouges pour éclairer la zone, produisant une image nette en noir et blanc. La portée de l’éclairage infrarouge est importante ; privilégiez les caméras capables de voir à au moins 9 mètres dans l’obscurité totale.
- Vision nocturne couleur : Technologie plus avancée, elle utilise des capteurs haute sensibilité et parfois un petit projecteur intégré pour capturer des vidéos en couleur la nuit. Les images en couleur peuvent révéler des détails essentiels, comme la couleur des vêtements d’une personne ou d’un véhicule, qui seraient invisibles sur une image en noir et blanc.
Pour les sites extérieurs critiques, une caméra dotée d'une vision nocturne couleur de haute qualité offre un niveau de sécurité et une capacité de collecte de preuves supérieurs.
Comment vos enregistrements seront-ils stockés ?
Votre caméra de sécurité filme en permanence, mais les enregistrements doivent être stockés quelque part. Vous avez généralement deux options : le stockage local ou le stockage dans le cloud. De nombreux systèmes modernes proposent les deux, pour une solution hybride.
Les avantages du stockage local
Le stockage local consiste à enregistrer la vidéo directement sur un support physique chez vous. La méthode la plus courante est l'utilisation d'une carte microSD insérée dans la caméra. Il s'agit d'un achat unique, sans frais récurrents. Vos enregistrements sont stockés de manière privée chez vous et restent accessibles même en cas de coupure internet (mais vous ne pouvez pas les visionner à distance sans connexion internet). Certains systèmes permettent également l'enregistrement sur un enregistreur vidéo réseau (NVR) ou une station de base domestique, capable de stocker des semaines, voire des mois, d'enregistrements continus provenant de plusieurs caméras.
La commodité du stockage en nuage
Le stockage cloud télécharge automatiquement vos clips vidéo sur un serveur distant géré par le fabricant de votre caméra. L'avantage principal ? Vos enregistrements sont protégés contre les dommages physiques et le vol. En cas de cambriolage, les images sont déjà stockées en toute sécurité hors site. Le stockage cloud vous permet également d'accéder facilement à vos clips et de les partager où que vous soyez grâce à une application pour smartphone.
Le principal inconvénient réside dans le coût. La plupart des fournisseurs facturent un abonnement mensuel ou annuel pour le stockage cloud, souvent avec des formules à plusieurs niveaux en fonction du nombre de caméras et de la durée de l'historique vidéo (par exemple, 7, 30 ou 60 jours). Il est important d'intégrer ces coûts récurrents à votre budget.
Quelles sont les fonctionnalités intelligentes qui comptent vraiment ?
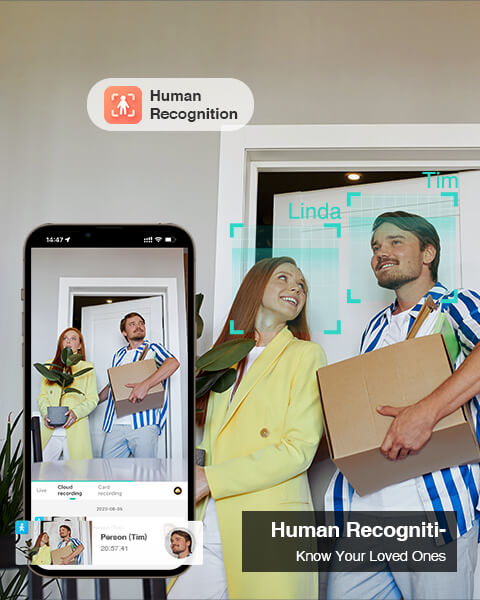
Les caméras de sécurité modernes sont bien plus que de simples enregistreurs passifs ; ce sont des appareils intelligents capables d'analyser ce qu'ils voient. La fonctionnalité intelligente la plus performante est la détection par intelligence artificielle . La détection de mouvement basique déclenche une alerte au moindre mouvement, ce qui entraîne une multitude de fausses alarmes dues au balancement des arbres, au passage des voitures ou aux animaux. Cela peut provoquer une « fatigue des alertes », vous incitant à ignorer complètement les notifications.
Les systèmes avancés, comme ceux de Botslab, utilisent une intelligence artificielle embarquée sophistiquée pour distinguer différents types de mouvements. Ils peuvent identifier une personne, un véhicule, un animal domestique ou un colis. Ainsi, vous pouvez configurer votre système pour qu'il vous avertisse uniquement lorsqu'une personne rôde sur votre porche, et non à chaque fois qu'un écureuil passe. Ce filtrage intelligent rend votre système de sécurité beaucoup plus utile et moins intrusif. Parmi les autres fonctionnalités intelligentes intéressantes, citons les zones d'activité, qui vous permettent de définir des zones spécifiques à surveiller (comme un portail ou une porte) tout en ignorant les mouvements dans d'autres (comme un trottoir public).
Qui installera le système ?
L'essor des technologies conviviales a fait de l'installation soi-même (DIY) l'option la plus populaire. Les caméras sans fil sont conçues pour une installation facile, qui ne prend souvent que quelques minutes par caméra. Le processus consiste généralement à fixer la caméra, à la connecter à votre réseau Wi-Fi via une application pour smartphone et à configurer les paramètres. L'installation soi-même permet de réaliser des économies et offre la possibilité de déplacer les caméras ou d'étendre votre système ultérieurement.
L'installation par un professionnel est généralement réservée aux systèmes PoE câblés complexes nécessitant le passage de câbles dans les murs et les combles. C'est également une excellente option pour les personnes peu à l'aise avec la technologie ou qui souhaitent faire installer et optimiser un système multicaméras de grande envergure pour une couverture parfaite. Bien qu'elle implique un coût initial supplémentaire, elle garantit une installation propre et fiable, sans aucun tracas de votre part.
Quels sont les coûts à long terme ?
Lors de l'établissement du budget pour un système de caméras de sécurité, il est essentiel de prendre en compte d'autres éléments que le prix initial du matériel. Le coût total de possession inclut les dépenses initiales et les frais d'entretien. Les dépenses initiales comprennent le prix des caméras, des fixations et de toute station de base ou hub nécessaire. Ce coût peut varier de moins de cent dollars pour une simple caméra intérieure à plusieurs milliers de dollars pour un système complet multicaméras 4K.
Les coûts récurrents concernent principalement les abonnements de stockage cloud. Ceux-ci peuvent varier de quelques euros par mois pour une seule caméra à plus de vingt euros pour un forfait multicaméra avec historique vidéo étendu. Si vous optez pour un système sans fil, il faut également prendre en compte le coût potentiel des batteries de remplacement, même si la plupart sont conçues pour durer toute la vie de la caméra. En choisissant un système doté d'options de stockage local performantes, vous pouvez réduire considérablement, voire éliminer, ces frais mensuels récurrents, ce qui en fait un investissement plus prévisible sur le long terme.



























Partager:
Quelle caméra de sécurité offre la meilleure autonomie pour une utilisation prolongée ?
Pourquoi la communication audio bidirectionnelle est-elle une fonctionnalité indispensable sur une sonnette vidéo ?